How Server Storage Area Networks Fit Into Modern Infrastructure?
In today’s world where significant strains are being placed on datacenters today, storage will always be one of the biggest concerns system administrators need to tackle in their daily routines. With an increased focus on performance optimization, especially on Linux servers as discussed previously, system administrators need to consider all possible options to improving their networks in order to avoid not keeping pace with the industry.

Although it isn’t something most professionals would think of immediately, server storage area networks are becoming one of the most cost effective ways to improve performance while still keeping your workload manageable.
What is a Server Storage Area Network?
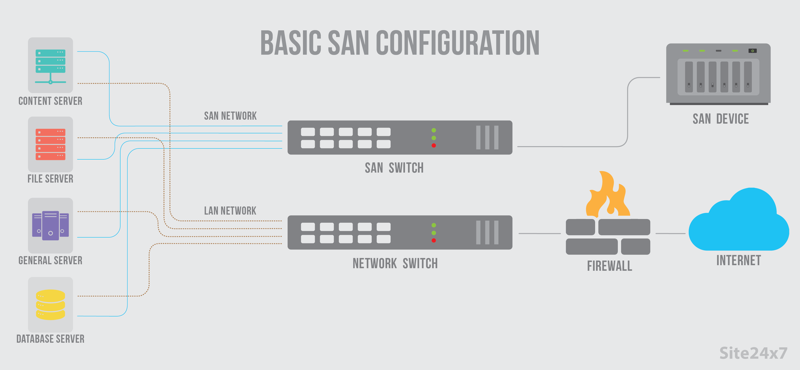
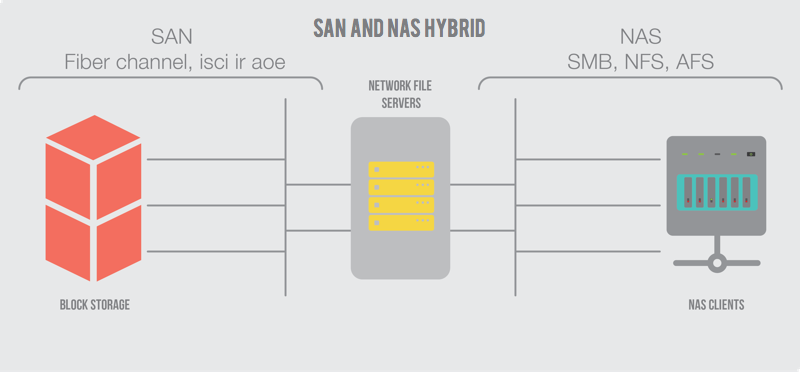
Storage area network (SAN) technology originated in the late 1990’s as a way to overcome the inefficiencies of direct attached storage (DAS). By centralizing data between machines, it became easier to move data across clusters – cutting the time from hours/days to seconds/minutes – making it possible for companies to improve capacity without sacrificing reliability. Rather than keeping data specific to a single device, SAN systems allow data to be sharable while also enabling multiple devices to pool their capacities.
Key Characteristics of Server SAN Systems
For a system to be considered a Server SAN package it must meet the following general criteria:
- The administrator should only have to worry about managing the storage systems rather than configuring ports and other network components
- The system must understand that performance aspects such that system administrators do not need an understanding of knobs or RAID types
- SAN systems must support multiple applications and volumes
- SAN systems should have the capability to optimize throughput to a single tenant
- Performance should be better than traditional SAN systems by having data near the processors as a way to reduce latency
Modern Improvements to Server SAN~Systems
Since the early days of these platforms, these arrays have evolved to include the adoption of flash storage, embraced automatic tiering technologies and more, making it easier to virtualize complex APIs. The biggest benefit of SAN systems for system administrators is that they reduce the overhead between the hypervisor and the storage arrays greatly boosting performance.
How it fits into Existing Systems
Server SANs are highly versatile allowing system administrators to roll out complex configurations such as the ones below which normally would not be possible with older technologies:
- High performance subnet: By having storage hold all critical data in flash, IO activities run much quicker allowing data to be processed 100x faster than traditional systems
- Big data subnet: By using knowledge of where data is stored, big data applications can be optimized to retrieve information rapidly regardless of the information set size
- Metadata subnet: As the need for physical security systems has increased, metadata subnets allow security professionals to sift through metadata rapidly to spot threats before they get out of hand
- Low cost file storage: A favorite of both businesses and the general public. This is made possible by allowing service providers to utilize low performance hardware to create large clusters for storage where speed isn’t a top priority
Coupling Performance Monitoring with Server SAN Storage
While purchasing quality SAN storage equipment is a great way to enhance your network performance, proper maintenance of such systems are vital to ensuring the equipment is functioning at peak levels as long as possible. Aside from ensuring equipment isn’t overloaded and that workloads are being distributed effectively between machines. By using a server monitoring solution administrators can track their entire IT infrastructure from a single location to simplify managing even the most complex systems.
Aside from helping to improve budgeting and equipment reliability, performance monitoring can be used to ensure that hardware cycles are structured to maximize cost efficiency while balancing work capacity.